Trigger point pressure
Acupressure treatment is a complete therapeutic approach that helps relieve pain, restore function, induce relaxation and achieve excellent health.
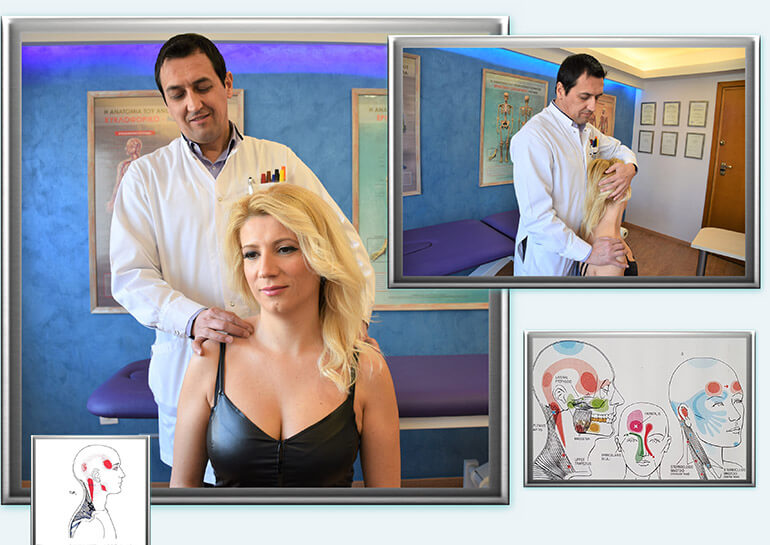
A muscle fascia Trigger Point is a hypersensitive point on a skeletal muscle located in the muscle tissue or associated fascia. It is painful under pressure and can cause a characteristic pain sensation and symptoms related to autonomic nervous system functions.
Types of trigger points
There are three types of trigger points causing muscle pain:
● Active (basic), the presence of which causes pain, restriction of movement, pain during pressure or after stretching of the muscle.
● Satellite trigger points, which can be created around an active trigger point and are not so painful. They disappear after the basic-active trigger point has been successfully treated.
● Latent trigger points, where some active trigger points may develop, resulting in joint movement restriction and muscle spasm, while sometimes they also cause pain. When does this happen? When a musculoskeletal problem (e.g. cervical stiffness) is treated with medication, conventional physiotherapy and rest, the patient initially shows improvement but after a short while the symptoms re-emerge, because the possible trigger points were not identified and subsequently deactivated during the treatment.
The pain path may not always be related to the span of the muscle.
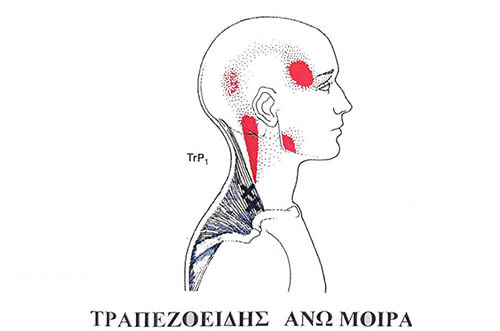
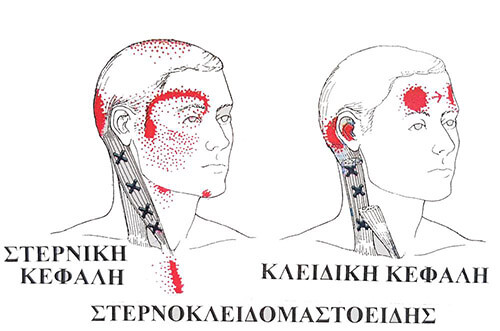
- Due to sudden overload.
- Due to overuse strain (long-term incorrect posture - stress).
- From direct trauma.
- Due to low temperatures.
- Indirect activation from arthritic joints, visceral damage and psychosomatic exhaustion.
- Immediate and improved function of the muscles and joints following ischemic pressure in specific parts of the muscle for 10 to 45 seconds.
- Application of stretching techniques after the completion of each pressure round; application of ice on the area and stretching of the muscle to regain its lost elasticity.
- Freeze Spray application disrupts the pain-contraction reflex arc and so we immediately achieve an increase in range of motion (R.O.M; measurement is done in degrees).
- Dry needling. Physiotherapists insert a sterile, thin and flexible, disposable needle into a trigger point, manipulating it manually to achieve faster muscle relaxation.
- Headaches
- Lumbago
- Sciatica
- Cervical spine syndrome
- Shoulder periarthritis
- Tendinopathy
- Limited mobility
- Frozen shoulder syndrome (stiffness of the shoulder and scapula) etc.