Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy is a therapeutic tool used in physiotherapy, based on the use of electricity on the body for therapeutic purposes.
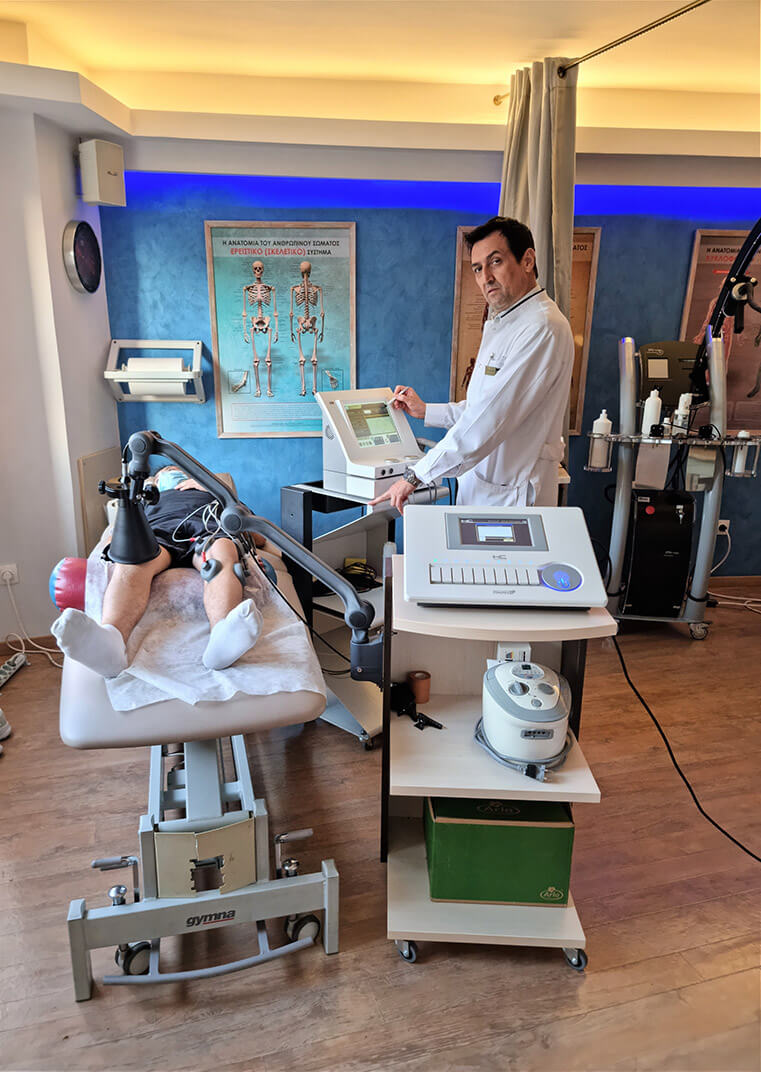
The use of different forms of electricity constitutes an excellent complementary physiotherapy practice for:
- Analgesia
- Anti-inflammatory and anti-spasmodic action.
- Muscle strengthening after atrophy (due to injury or surgery).
- Nerve paralysis (facial nerve paralysis, brachial plexus paralysis, etc.)
Tens
TENS is one of the most modern analgesic therapeutic currents. Its effect on the central nervous system to reduce or inhibit pain is due to the following mechanisms:
- Gate Theory
- ControlProduction of enkephalins
- Production of B-endorphin
TENS burst:
Activation of Trigger Points, acupuncture points and reflex zones
Intereferential currents
When applied correctly, they provide the potential for antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic action.
Specialized currents
Russian and MF:
For atrophies following surgery or injuries.
Triangular galvanic and Faradic current:
- Specialized currents for nerve paralysis (facial nerve paralysis, brachial plexus paralysis.
- Neurapraxia and axonotmesis.
- Neurotmesis (following rehabilitation after surgery).
Iontophoresis:
The therapeutic method that allows for the penetration of ions of a water-soluble pharmaceutical substance through the skin with the help of continuous galvanic current.
Mode:
The pharmaceutical substance acts more effectively in the targeted area.
It is a direct, painless technique, free of injury or infection risks. Depending on each specific case, different pharmaceuticals can be used.
We achieve:
- Anti-inflammatory action (muscle and bursae inflammation).
- Analgesic action (arthritis, myalgias, bursitis, neuritis).
- Anti-edematous action (edemas - hematomas).
- Wound - skin ulcers healing, scar tissue normalization.
- Cervical spine syndrome
- Lower back pain, sciatica, intervertebral disc herniation.
- Shoulder periarthritis, tendinopathy (tendinitis).
- Muscle and tendon injuries, sprains.
- Hip and knee osteoarthritis.
- Fractures.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, muscle and tendon dysfunctions.